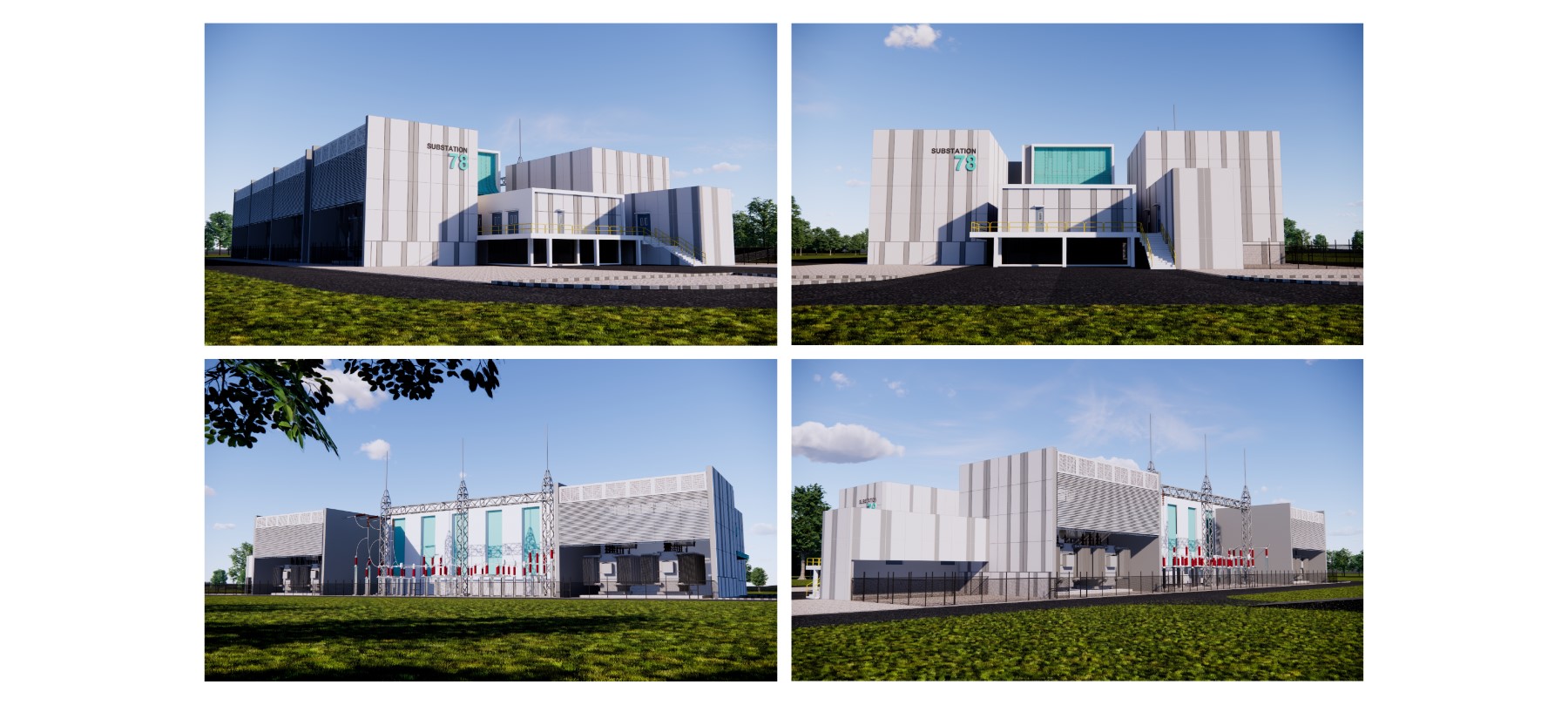
In the heart of Sarawak, a quiet transformation is underway in Bintulu. The PETRONAS LNG Complex (PLC) - operated by Malaysia LNG Sdn Bhd (MLNG), will undergo plant electrification as part of the company’s efforts to decarbonise its operations. This complex has nine LNG production trains, making it one of the top five largest LNG plants in the world. The PLC can produce up to 29.8 million tonnes of LNG per year, which is equivalent to the energy consumption of around 10 million homes1.
Electrification is a way to lower GHG emissions through the process of switching from fossil fuel-based energy sources to electricity generated from renewable sources, such as solar, wind, and hydropower2. For PETRONAS, electrification is one of the four levers to achieve its Net Zero Carbon Emissions 2050 aspiration. One of the initiatives is to generate electricity for MLNG plants using hydroelectric power in place of fuel gas.
Project G.L.O.R.Y - Gain in LNG by Outsourcing from Renewable Energy
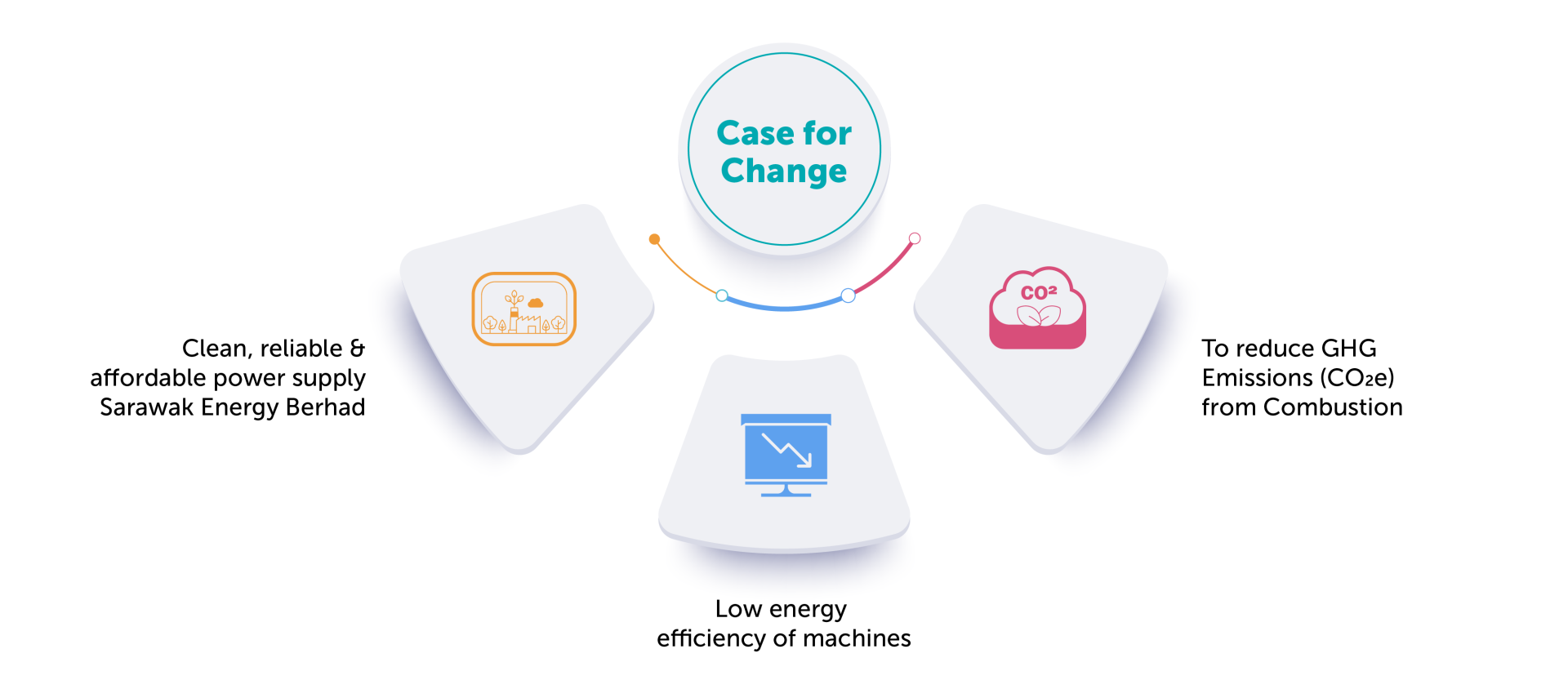
Enter Project GLORY – an initiative mooted in 2019 to reduce the usage of natural gas to fuel the plants. Therefore, instead of relying solely on gas-powered turbines, PLC will be supplied partially with electricity generated by hydropower from the Sarawak main grid. The decision to electrify the PLC was driven by the following factors:
- To obtain clean and reliable power supply from the Sarawak Energy operated State Power Grid with low GHG index of 0.213 tCO2/MWh.
- To reduce GHG emissions (CO2e) from the combustion in MLNG which generates a GHG index of 0.916 tCO2e/MWh.
- To retire low efficiency electricity generators which contributes to significant CO2 emissions.